Embark on an intellectual odyssey with AP Psychology Unit 6 FRQ, where the intricacies of social psychology unravel before your very eyes. This captivating journey explores the depths of human cognition, influence, and behavior, promising an unforgettable exploration of the mind’s social landscape.
Social psychology, the cornerstone of Unit 6 FRQ, unveils the profound impact of social forces on our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Prepare to delve into the complexities of social cognition, the ways in which we perceive, interpret, and remember social information.
Uncover the multifaceted nature of social influence, from conformity to persuasion, and witness its transformative power in shaping human behavior.
Define and Explain Key Concepts
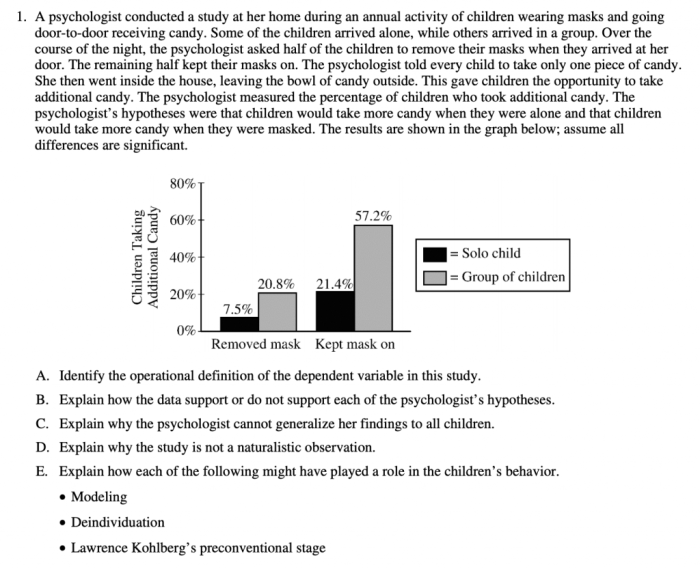
Social psychology, the focus of Unit 6 FRQ, is the study of how our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others.
Social cognition, a key concept in social psychology, refers to the mental processes that we use to perceive, interpret, and remember social information. It helps us understand how we make sense of our social world and how we interact with others.
Social Influence
Social influence refers to the ways in which others can affect our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It can take various forms, including:
- Conformity:Changing our behavior or beliefs to match those of the group.
- Obedience:Following the orders of an authority figure, even if they conflict with our own beliefs.
- Social facilitation:Improving our performance on tasks when we are in the presence of others.
- Social loafing:Reducing our effort on tasks when we are working with others.
Analyze Research Methods
In social psychology, researchers employ a range of methods to investigate human behavior and mental processes in social contexts. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, shaping the researcher’s approach and the validity of the findings.
Observational Methods
Observational methods involve observing and recording behavior in natural settings or controlled environments. They provide insights into behavior in real-world contexts.
- Naturalistic observation:Observing behavior in natural settings without intervening.
- Participant observation:Observing behavior while actively participating in the setting.
- Controlled observation:Observing behavior in a controlled environment, manipulating variables to isolate their effects.
Advantages:High ecological validity, capturing behavior in its natural context.
Limitations:Observer bias, difficulty in controlling variables, and potential for reactivity from participants.
Experimental Methods
Experimental methods involve manipulating variables to determine their effects on behavior. They provide strong evidence of causality.
- Laboratory experiment:Conducted in a controlled environment, with random assignment of participants to conditions.
- Field experiment:Conducted in a natural setting, with random assignment of participants to conditions.
Advantages:High internal validity, control over variables, and ability to establish causality.
Limitations:Artificiality of laboratory settings, difficulty in generalizing findings to real-world contexts.
Survey Methods, Ap psychology unit 6 frq
Survey methods involve collecting data from a large sample of people using questionnaires or interviews. They provide insights into attitudes, beliefs, and experiences.
- Cross-sectional survey:Collecting data from a sample at one point in time.
- Longitudinal survey:Collecting data from the same sample over time.
Advantages:Can reach a large sample, provide a wide range of data, and allow for comparisons between groups.
Limitations:Self-report bias, difficulty in ensuring representativeness, and potential for social desirability effects.
Correlational Methods
Correlational methods examine the relationship between variables without manipulating them. They provide insights into associations, but not causality.
- Correlation coefficient:Measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
- Regression analysis:Examines the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
Advantages:Can identify relationships between variables, useful for exploratory research.
Limitations:Cannot establish causality, can be influenced by confounding variables.
Discuss Ethical Considerations: Ap Psychology Unit 6 Frq
In conducting social psychology studies, researchers are bound by ethical guidelines to ensure the well-being and protection of participants. These guidelines are crucial to maintain the integrity and validity of research findings while upholding ethical principles.
Informed Consent
Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants before involving them in any study. This means providing potential participants with clear and comprehensive information about the study’s purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. By providing informed consent, participants can make informed decisions about their participation, ensuring their autonomy and respect for their rights.
Confidentiality
Researchers have a responsibility to maintain the confidentiality of participant information. This includes protecting the anonymity or privacy of participants, ensuring that their data is kept secure and confidential. By upholding confidentiality, researchers foster trust and protect participants from potential harm or embarrassment.
Protecting Participants from Harm
Researchers must take all reasonable steps to protect participants from physical, psychological, or social harm. This includes conducting studies in a safe and ethical manner, minimizing potential risks, and providing appropriate support or referral services to participants who may experience distress or discomfort during the study.
Ethical Dilemmas in Unit 6 FRQ Topics
In unit 6 FRQ topics, researchers may encounter ethical dilemmas that require careful consideration. For instance, studies involving deception or manipulation of participants raise concerns about informed consent and potential harm. Researchers must carefully weigh the potential benefits of the study against the risks to participants and strive to find alternative methods that minimize ethical concerns.
Design and Conduct a Research Study
Conducting a research study in social psychology involves a systematic process that requires careful planning and execution. By following a step-by-step guide, researchers can ensure the validity and reliability of their findings.
AP Psychology Unit 6 FRQ can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can be mastered. One way to improve your understanding of the material is to connect it to real-world examples. For instance, the concept of conditioning can be illustrated through the d minor scale bass clef , where the repeated practice of playing the notes reinforces the connection between the stimulus and the response.
By applying this principle to your studies, you can enhance your comprehension of AP Psychology Unit 6 FRQ.
The first step is to formulate a research question. This question should be specific, testable, and relevant to the field of social psychology. Once the research question is defined, researchers must choose an appropriate research method. The most common methods include surveys, experiments, and naturalistic observation.
Data Collection
The next step is to collect data. This involves selecting a sample of participants who are representative of the population being studied. Researchers must also develop a data collection instrument, such as a survey or questionnaire. The data collection process should be standardized to ensure that all participants are treated equally.
Data Analysis
Once the data is collected, it must be analyzed to determine whether the research question has been answered. Researchers use statistical tests to analyze the data and determine whether the results are statistically significant. It is important to use appropriate statistical tests and to interpret the findings accurately.
Conclusion
The final step is to write a research report that describes the study’s purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. The report should be clear and concise, and it should be written in a way that is accessible to both researchers and non-researchers.
Apply Social Psychology to Real-World Issues

Social psychology provides valuable insights into human behavior and social interactions, enabling us to understand and address real-world issues. By applying social psychology theories and research, we can develop effective interventions and policy decisions that promote social well-being and address societal challenges.
Identifying Real-World Issues
Social psychology can be applied to a wide range of real-world issues, including:
- Intergroup conflict and prejudice
- Prosocial behavior and helping
- Persuasion and attitude change
- Health behavior and well-being
- Environmental sustainability
Informing Interventions and Policy Decisions
Social psychology research provides evidence-based insights that can inform the design and implementation of interventions and policy decisions. For example, research on intergroup conflict has shown that contact between different groups can reduce prejudice and promote understanding. This knowledge has been used to develop interventions such as intergroup contact programs and diversity training.
Successful Applications
Social psychology has been successfully applied to address various societal challenges:
- Reducing prejudice and discrimination
- Promoting healthy behavior
- Encouraging environmental sustainability
- Improving communication and conflict resolution
- Enhancing workplace productivity
Query Resolution
What is the significance of social cognition in understanding human behavior?
Social cognition plays a pivotal role in shaping our perceptions, interpretations, and memories of social information. It influences how we process and respond to social cues, make judgments about others, and form relationships.
How can social influence manifest itself in different forms?
Social influence takes on various forms, including conformity, obedience, and persuasion. Conformity refers to the tendency to adjust our behavior to match the actions of others, while obedience involves following the commands of an authority figure. Persuasion, on the other hand, involves changing attitudes or behaviors through communication and argumentation.
What are the ethical considerations that researchers must adhere to in social psychology studies?
Researchers in social psychology are bound by ethical guidelines to protect the rights and well-being of participants. These guidelines include obtaining informed consent, ensuring confidentiality, and minimizing potential harm or discomfort.